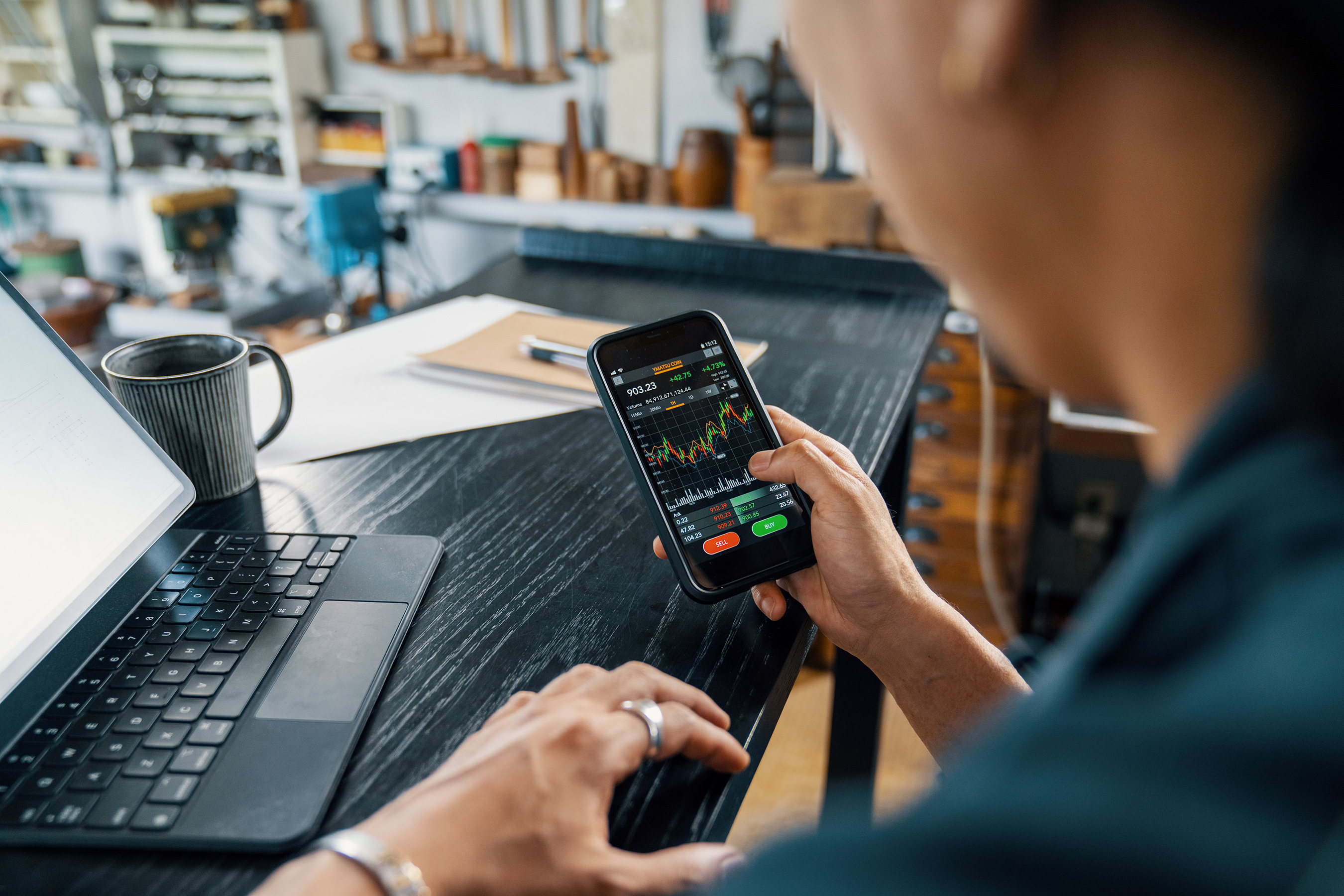
Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange trading, is the process of buying and selling currencies on the global market. It offers individuals and institutions the opportunity to profit from the fluctuations in currency values. The Forex market is the largest financial market in the world, with an average daily trading volume exceeding $6 trillion. Whether you're just starting or looking to refine your trading skills, understanding the fundamentals of Forex trading is key to navigating this dynamic and fast-paced market.
Understanding Forex Trading Basics
The Forex market offers unique opportunities for traders to engage in the exchange of global currencies. To grasp the mechanics of Forex trading, it's essential to understand its core concepts and how it operates.
1. What is Forex Trading?
Forex trading refers to the exchange of one currency for another, aiming to profit from fluctuations in currency prices. The Forex market is decentralized, meaning there is no central exchange. It operates 24 hours a day across different time zones, making it one of the most liquid markets in the world. Major currency pairs, such as EUR/USD and GBP/USD, dominate the trading volumes.
The Forex market facilitates global trade and investment by enabling companies to convert foreign currency for cross-border transactions.
Retail traders also participate in Forex trading through online platforms, connecting them to global liquidity pools.
2. How Does Forex Trading Work?
Forex trading revolves around buying one currency and selling another simultaneously, forming a currency pair. The bid price is the price at which traders can sell a currency, while the ask price is the price at which they can buy.
The difference between these prices is known as the spread.
A trader's goal is to predict the movement of currency prices to profit from price changes.
Example: If you buy the EUR/USD pair at 1.1200 and sell it later at 1.1300, you make a profit of 100 pips.
3. The Role of Currency Pairs in Forex Trading
Currency pairs are the foundation of Forex trading. Each pair consists of two currencies: the base currency (first) and the quote currency (second).
<1> EUR/USD - The Euro is the base currency, and the US Dollar is the quote currency.
<2> GBP/USD - The British Pound is the base currency, and the US Dollar is the quote currency.
<3> USD/JPY - The US Dollar is the base currency, and the Japanese Yen is the quote currency.
Currency pairs are classified as major, minor, or exotic based on their trading volume and popularity.
Major pairs are highly liquid, while exotic pairs can have wider spreads and higher risk.
4. Types of Forex Markets: Spot, Futures, and Options
In the Forex market, there are several trading formats:
Spot Market: The most common market for Forex trading, where currencies are exchanged immediately at the current market price.
Futures Market: Involves trading standardized contracts to buy or sell currency at a predetermined price in the future.
Options Market: Provides traders the right, but not the obligation, to exchange currencies at a set price before a specific expiration date.
5. Key Players in Forex Trading: Banks, Brokers, Retail Traders
Several key players influence the dynamics of the Forex market:
Banks: Large international banks are the most significant participants, facilitating the largest trades in the market.
Brokers: Online Forex brokers act as intermediaries for retail traders, offering access to liquidity pools and trading platforms like MetaTrader 4 and MetaTrader 5.
Retail Traders: Individual traders participate using smaller capital but can access high leverage through brokers.
Each of these players contributes to the price discovery process and impacts overall market liquidity.
Popular Forex Trading Strategies
Successful traders rely on various strategies to navigate the dynamic Forex market. Understanding these strategies helps traders identify the best approach based on their risk tolerance, time commitment, and market analysis skills.
1. Scalping in Forex Trading
Scalping is a popular strategy that involves making quick, small profits by opening and closing multiple positions throughout the day. This strategy is typically employed on lower timeframes (e.g., 1-minute or 5-minute charts).
Target: Small price movements, often just a few pips.
Timeframe: Ultra-short term trades, holding positions for seconds or minutes.
Risk Level: High, due to the rapid pace of trades and frequent exposure.
Key Indicators Used:
Moving Average for trend direction.
RSI (Relative Strength Index) for identifying overbought or oversold conditions.
2. Day Trading: Maximizing Intraday Opportunities
Day trading involves opening and closing trades within the same trading day, ensuring no overnight risk exposure. This strategy takes advantage of intraday price fluctuations, typically focusing on higher timeframes like the 15-minute or 1-hour charts.
<1> Entry Criteria: Based on technical analysis (e.g., MACD, Stochastic Oscillator).
<2> Exit Criteria: Traders exit positions before the end of the trading session, often using stop-loss orders to manage risk.
3. Swing Trading: Capturing Medium-Term Price Movements
Swing trading focuses on capturing larger price movements over several days or weeks, making it ideal for those who cannot monitor the markets constantly.
Entry: Usually based on technical patterns (e.g., head and shoulders, triangles).
Exit: Traders look for significant trend reversals or reaching key support/resistance levels.
Pros:
More time for analysis compared to day trading.
Lower stress levels, as positions are held for days.
4. Position Trading: Long-Term Forex Strategy
Position trading is for those with a long-term perspective, holding trades for weeks, months, or even years. This strategy is suitable for traders who focus on fundamental analysis to predict long-term currency movements.
Key Tools: Economic indicators such as GDP growth, interest rate decisions, and inflation reports.
Example: Holding positions through major economic shifts, such as central bank policy changes.
5. Trend Following: Riding the Market Waves
Trend following is based on the idea that currencies that are trending in one direction will continue to do so for some time. Traders using this strategy identify trends and aim to ride them until a reversal signals the end of the trend.
Tools Used:
Bollinger Bands: To gauge market volatility.
Fibonacci Retracement: For spotting potential reversal levels.
Forex Trading Tools and Platforms
Forex traders rely on various tools and platforms to execute trades efficiently and make informed decisions. Whether you are analyzing the market, managing trades, or optimizing strategies, the right tools are essential for success.
1. MetaTrader 4: The Industry Standard
MetaTrader 4 (MT4) is one of the most popular trading platforms among Forex traders. Known for its user-friendly interface and a comprehensive suite of trading tools, MT4 is ideal for both beginners and experienced traders.
Key Features:
Charting tools: Customizable charts with multiple indicators like Moving Averages and RSI.
Expert Advisors (EAs): Automated trading systems that help you trade without constant supervision.
Multiple order types: Allows you to set Stop-Loss and Take-Profit orders to manage risk.
MT4 is widely supported by Forex brokers such as OANDA and FXCM and offers seamless integration with most currency pairs.
2. MetaTrader 5: Advanced Features for Pro Traders
MetaTrader 5 (MT5) is the successor of MT4 and brings advanced features for experienced traders who need more analytical tools and deeper market access.
<1> New Asset Classes: Supports stocks, futures, and commodities alongside Forex.
<2> Improved Order Management: Advanced order types like Fill or Kill and Immediate or Cancel.
<3> Market Depth: Allows traders to view the market's liquidity levels for better price forecasting.
Pros:
Optimized for multi-asset trading.
Faster execution and more indicators compared to MT4.
Access to economic events data like GDP growth or interest rate decisions.
3. TradingView: The All-In-One Charting Tool
TradingView is a web-based platform known for its intuitive interface and a powerful set of charting tools. It is favored by traders who rely on technical analysis and market sentiment.
Collaborative Tools: Allows traders to share ideas and analysis with the community.
Custom Indicators: Users can create their own indicators or access those created by others.
Real-Time Data: Instant market updates for accurate trade execution.
4. cTrader: For the Modern Trader
cTrader is another popular platform, known for its modern interface and fast execution speeds.
Key Features:
Level II Pricing: View the bid/ask prices at various levels for better order execution.
Chart Customization: Allows extensive customization for technical traders.
One-Click Trading: Place trades instantly with a single click.
5. Risk Management Tools: Stop-Loss, Take-Profit, and More
Effective risk management is essential in Forex trading. Platforms like MT4 and MT5 allow you to integrate tools like Stop-Loss Orders and Take-Profit Orders to minimize potential losses.
<step 1> Stop-Loss: Automatically closes a trade when the market moves against you by a certain number of pips.
<step 2> Take-Profit: Locks in profits by closing a position when it reaches your target price.
<step 3> Position Sizing: Determines the amount to trade based on your risk tolerance, ensuring you don’t risk more than a predetermined percentage of your account balance.
| Risk Management Tool | Description | Platform Support |
|---|---|---|
| Stop-Loss | Limits losses by closing positions at a specific price | MT4, MT5, cTrader |
| Take-Profit | Automatically locks in profits once a target is hit | MT4, MT5, TradingView |
| Position Sizing | Calculates the optimal position size based on risk tolerance | MT4, MT5, cTrader |
Forex Market Analysis
Forex market analysis is crucial for making informed trading decisions. Traders use various approaches to analyze the market, including fundamental analysis, technical analysis, and sentiment analysis. These methods help predict currency price movements and identify profitable opportunities.
1. Fundamental Analysis: Understanding Economic Drivers
Fundamental analysis involves examining economic, financial, and political factors that influence currency values. This analysis is often used by traders engaging in position trading or swing trading, as it focuses on long-term trends.
Interest Rate Decisions: Central banks’ decisions on interest rates (e.g., USD/JPY pair) directly affect currency values.
Economic Data: Reports such as Nonfarm Payrolls (NFP), GDP growth, and retail sales influence market sentiment.
Geopolitical Events: Elections, wars, or trade negotiations can impact currency volatility.
Traders using fundamental analysis rely on data and events to predict future market trends. By following economic reports and central bank meetings, traders can make informed decisions about the value of currency pairs like EUR/USD or GBP/USD.
2. Technical Analysis: Predicting Price Movements
Technical analysis is the study of historical price movements using charts and indicators to forecast future market trends. Traders rely on tools such as Moving Averages, Bollinger Bands, and Fibonacci Retracements.
Key Indicators:
RSI (Relative Strength Index): Measures whether a currency pair is overbought or oversold.
MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence): Helps identify potential buy or sell signals.
Stochastic Oscillator: Indicates market momentum and potential reversal points.
3. Sentiment Analysis: Understanding Market Psychology
Sentiment analysis focuses on the collective mood of the market, helping traders understand the psychology behind price movements. This analysis involves gauging whether market participants are generally optimistic or pessimistic about a currency pair.
<step 1> Market Surveys: Traders look at reports from Forex brokers like Pepperstone and FXCM to gauge market sentiment.
<step 2> News and Social Media: Major news stories, social media platforms, and news outlets often impact the mood of traders.
<step 3> Economic Events: Events like interest rate decisions can dramatically shift market sentiment, making sentiment analysis an essential tool for short-term traders.
| Sentiment Indicator | Description | Relevance for Forex Trading |
|---|---|---|
| COT Report (Commitment of Traders) | Reports on market positions taken by different trader types | Identifies trends in long/short positions |
| News Sentiment Analysis | Evaluation of news stories and headlines for market mood | Helps determine bullish or bearish sentiment |
| Forex Flow Data | Tracking currency flows across exchanges | Provides insights into major market movements |
4. Combining the Three Approaches: A Holistic View
Integrating fundamental, technical, and sentiment analysis offers a more comprehensive view of the market. For instance, a trader might observe a positive economic report (fundamental) while using technical indicators to spot an entry point and employing sentiment analysis to gauge overall market enthusiasm.
This multi-layered approach can provide traders with a stronger foundation for making Forex trading decisions, whether they are focusing on day trading or trend following strategies.
By mastering these three core methods, traders can become adept at navigating the complexities of the Forex market, ensuring they are well-prepared for any conditions that arise.
Risk Management in Forex Trading
Effective risk management is essential for successful Forex trading. Traders use various strategies to minimize losses while maximizing potential gains. Risk management techniques such as stop-loss orders, take-profit orders, and position sizing help maintain a balance between risk and reward in volatile Forex markets.
1. Stop-Loss Order: Protecting Your Capital
A stop-loss order automatically closes a trade when a currency pair reaches a certain price level, preventing excessive losses. It's a crucial tool in day trading, scalping, and swing trading.
Advantages:
Protects capital by limiting losses.
Provides peace of mind by automating risk control.
Allows for emotional detachment in volatile markets.
Example: A trader buys GBP/USD at 1.3800 and sets a stop-loss at 1.3750 to limit the potential loss to 50 pips.
2. Take-Profit Order: Locking in Profits
A take-profit order automatically closes a trade when a predetermined profit level is reached. It helps traders capture gains without needing constant market monitoring.
Advantages:
Ensures profits are realized at a specific price point.
Removes emotional decision-making from the process.
Enables traders to set multiple take-profit targets for diversified risk.
<step 1> Set a take-profit target based on technical indicators (e.g., Bollinger Bands or Fibonacci Retracement).
<step 2> Use fundamental analysis to predict the potential price direction of currency pairs like USD/JPY.
<step 3> Implement the take-profit order at a logical price level based on historical data or market trends.
3. Position Sizing: Managing Risk Exposure
Position sizing refers to the amount of capital a trader allocates to a specific trade. Correctly sizing a position helps control risk and ensures that no single trade will significantly impact the overall account balance.
| Risk Exposure | Formula for Position Sizing | Example for EUR/USD Trade |
|---|---|---|
| Low Risk | Account Equity × Risk Percentage ÷ Stop Loss Distance | $10,000 × 2% ÷ 50 pips = 4 micro lots |
| Medium Risk | Account Equity × Risk Percentage ÷ Stop Loss Distance | $10,000 × 3% ÷ 50 pips = 6 micro lots |
| High Risk | Account Equity × Risk Percentage ÷ Stop Loss Distance | $10,000 × 5% ÷ 50 pips = 10 micro lots |
Example: A trader with a $10,000 account size and 50 pips of risk per trade can adjust their position size to manage the risk and reward ratio effectively.
4. Risk-Reward Ratio: A Key to Profitability
The risk-reward ratio helps determine the potential profit compared to the potential loss in any trade. A favorable risk-reward ratio ensures that traders can remain profitable in the long term.
Ideal Risk-Reward Ratio: Most traders aim for a minimum ratio of 1:2 (risking 1 unit of currency to gain 2 units). This ensures that even if half of trades result in losses, overall profitability is achievable.
By calculating the risk-reward ratio before entering a trade, traders can ensure that the potential reward justifies the risks taken. This is especially crucial in volatile markets like AUD/USD and NZD/USD.
5. Margin: Understanding Leverage and Its Risks
Margin allows traders to control a large position with a relatively small amount of capital. While margin can increase profits, it also magnifies potential losses, making it essential to understand leverage and its implications.
Example: A 1:50 leverage means that with $1,000, a trader can control a position worth $50,000. This increases both potential profits and the risk of loss.
Traders must manage margin effectively, ensuring that they don't over-leverage their account, which could lead to forced liquidation if the market moves against them.
6. Monitoring Economic Events: Adjusting Risk in Real-Time
Economic events, such as interest rate decisions, Nonfarm Payrolls (NFP), and inflation reports, can cause sudden volatility in Forex markets. Traders should adjust their risk management strategies before and after significant news releases.
<step 1> Track upcoming economic events related to currency pairs like USD/JPY or GBP/USD.
<step 2> Prepare by reducing position sizes or setting wider stop-loss orders ahead of volatile announcements.
<step 3> Analyze market reactions post-event and adjust trades accordingly.
Effective risk management in Forex trading is about controlling potential losses, setting achievable targets, and managing exposure. By incorporating strategies like stop-loss orders, take-profit orders, position sizing, and risk-reward ratios, traders can navigate the complexities of the Forex market more confidently and profitably.
Choosing a Forex Broker
Selecting the right Forex broker is essential for successful trading. A good broker offers a reliable platform, low fees, and high liquidity for currency pairs like EUR/USD or GBP/USD. Below are key factors to consider when making your decision.
1. Regulatory Compliance and Reputation
Choosing a regulated Forex broker ensures that your funds are safe and that the broker adheres to financial standards.
Benefits of regulation:
Protects against fraud and ensures financial transparency.
Brokers must meet capital requirements and operate within set standards.
Regulated brokers are subject to audits and oversight by authorities such as FCA (Financial Conduct Authority) or ASIC (Australian Securities and Investments Commission).
2. Trading Platforms: User Experience and Tools
The trading platform provided by a Forex broker should be easy to use and offer the necessary tools for technical and fundamental analysis.
Popular platforms:
MetaTrader 4 (MT4) and MetaTrader 5 (MT5): Known for their user-friendly interface and vast library of technical indicators like RSI and MACD.
cTrader: Known for its advanced charting capabilities and fast execution speeds.
TradingView: Offers detailed charting features and social trading integration.
<step 1> Ensure the platform supports automated trading if you're using scalping or position trading strategies.
<step 2> Evaluate whether the platform provides integrated economic news for real-time trading decisions on pairs like USD/JPY.
<step 3> Test the platform with a demo account before committing real funds.
3. Trading Costs and Fees
Forex brokers often charge different types of fees that can significantly impact your profitability. Understanding these fees is crucial before committing.
| Fee Type | Description | Example for EUR/USD Trade |
|---|---|---|
| Spreads | The difference between buy and sell prices | Spread of 1.5 pips for EUR/USD |
| Commissions | Flat fee or percentage per trade | $5 per 100k traded in EUR/USD |
| Swap Rates | Interest rate differential for holding positions overnight | Swap of -0.3 pips for overnight holding of EUR/USD |
Example: A trader may incur a spread of 1.5 pips when trading EUR/USD, as well as additional commissions depending on the broker's fee structure.
4. Customer Support: Availability and Expertise
Responsive customer support is crucial in the event of technical issues or trade inquiries.
Key features to look for:
24/7 support availability, especially for traders in different time zones.
Multiple contact methods (chat, email, phone).
Support staff with expertise in Forex market nuances and trading platforms like MetaTrader 5.
5. Leverage and Margin Requirements
Leverage allows traders to control a larger position with a smaller amount of capital. Brokers offer varying leverage ratios, which can impact your risk exposure.
Important considerations:
High leverage (e.g., 1:500) can amplify both potential gains and losses, making it crucial for managing risk.
Ensure that margin requirements are clearly defined and comply with your risk tolerance levels.
6. Account Types and Deposit/Withdrawal Methods
Most brokers offer multiple account types, which may include demo accounts, standard accounts, and accounts with lower spreads for professional traders.
Account features to look for:
Demo accounts to practice with virtual money before trading real capital.
Fast, low-cost deposit and withdrawal options (e.g., PayPal, bank wire, or cryptocurrency).
Low minimum deposit requirements to begin trading.
Choosing the right Forex broker is a foundational decision in any trading strategy, from scalping to swing trading. By focusing on regulated brokers, robust platforms, and transparent fees, you ensure a smoother and more secure trading experience in volatile markets like USD/CHF or AUD/USD.
Conclusion
Navigating the world of Forex trading can seem overwhelming at first, but by understanding key concepts like currency pairs, different trading strategies, and effective risk management, you can build a strong foundation for successful trading. As you gain experience and become familiar with technical indicators and trading platforms, you'll be better equipped to make informed decisions that align with your financial goals. Whether you're trading EUR/USD or exploring more advanced strategies like scalping or swing trading, it's crucial to stay updated on market trends and economic events. With the right tools, strategies, and a solid risk management plan, you can navigate the dynamic Forex market with confidence.