In the dynamic world of global finance, the forex market stands out as a key player in shaping economic outcomes. One of the most significant factors driving forex market fluctuations is the changing levels of income across nations. As income levels rise or fall, they have a profound impact on consumer behavior, economic growth, and, ultimately, the demand for different currencies. This interplay between income changes and currency values is critical for traders and investors who are looking to navigate the complexities of foreign exchange markets. Understanding how income levels influence forex fluctuations can offer valuable insights for making informed investment decisions.
The Role of Economic Indicators in Forex Market Fluctuations
Understanding how various economic indicators influence the forex market can provide a clearer picture of currency fluctuations. These indicators offer insights into a country's economic health, investor behavior, and central bank policies, all of which have direct effects on currency values.
1: Interest Rates and Forex Market Fluctuations
Interest rates set by central banks are critical drivers of currency value in the forex market. When a central bank adjusts interest rates, it directly influences the flow of capital into or out of a country, altering demand for its currency. Higher interest rates tend to attract foreign investment, driving up the currency's value, while lower rates can lead to depreciation as investors seek better returns elsewhere.
Higher interest rates: Boost demand for the currency, leading to appreciation (e.g., USD/JPY).
Lower interest rates: Diminish currency demand, causing depreciation (e.g., EUR/USD).
Central Bank Actions: The Federal Reserve, European Central Bank (ECB), and Bank of Japan (BOJ) are key players in setting rates and influencing forex market fluctuations.
2: Inflation and Currency Value
Inflation significantly impacts the purchasing power of a currency, which in turn affects its exchange rate. As inflation rises, a currency tends to weaken due to reduced purchasing power, and traders often react by selling the currency. Central banks, including the Federal Reserve and ECB, may raise interest rates to combat high inflation, indirectly influencing forex market movements.
High inflation: Causes currency depreciation as the real value of money erodes.
Low inflation: Encourages currency appreciation due to maintained purchasing power.
Policy Response: Central banks often adjust interest rates to manage inflation, directly influencing currency value.
3: GDP Growth and Economic Health
A country's GDP growth is one of the most important indicators of its economic strength and influences forex market fluctuations significantly. Positive GDP growth signals a healthy economy, which typically strengthens its currency. Conversely, stagnation or contraction can lead to a decline in currency value.
Strong GDP growth: Attracts foreign investment, boosting currency strength (e.g., USD/CAD).
Weak or negative GDP growth: Leads to reduced investor confidence, weakening currency value (e.g., GBP/USD).
Investment Sentiment: Traders often analyze GDP growth in relation to other economic indicators to predict future forex movements.
4: Unemployment Rate as a Forex Indicator
The unemployment rate is a critical gauge of economic health and can have a significant impact on the forex market. A high unemployment rate suggests economic weakness, which can lead to reduced investor confidence and a weaker currency. On the other hand, low unemployment is typically seen as a sign of a growing economy, which can lead to currency appreciation.
High unemployment: Often results in a weaker currency as it signals economic instability (e.g., EUR/USD).
Low unemployment: Can strengthen a currency by signaling a prosperous economy (e.g., USD/JPY).
Central Bank Policy: Central banks may take action if unemployment remains high, such as lowering interest rates to stimulate growth.
5: Consumer Confidence and Forex Trends
Consumer confidence reflects the public's outlook on the economy and can be an early indicator of future economic performance. A high level of consumer confidence generally supports a strong currency, as it suggests that people are willing to spend and invest. Conversely, low consumer confidence can lead to reduced spending and investment, resulting in currency depreciation.
High consumer confidence: Signals economic optimism and strengthens currency values (e.g., AUD/USD).
Low consumer confidence: Signals economic uncertainty, leading to currency weakness (e.g., USD/TRY).
Economic Forecasting: Traders use consumer confidence indices to predict future economic trends and forex market movements.

Central Banks and Forex Market Influence
Central banks wield significant power over the forex market through their monetary policies, including interest rate decisions and other economic measures. Understanding the role of major central banks such as the Federal Reserve, the European Central Bank (ECB), and the Bank of England (BoE) can provide insights into how currency pairs like USD/JPY, EUR/USD, and GBP/USD fluctuate in the global market.
1: Federal Reserve (Fed) and USD Fluctuations
The Federal Reserve's decisions regarding interest rates and monetary policy have a profound impact on the USD. For instance, when the Fed raises interest rates, it tends to make the U.S. dollar more attractive to investors, increasing demand and driving up its value.
Interest rate hikes: Typically strengthen the USD, as higher rates attract foreign capital.
Interest rate cuts: Lead to weaker USD as lower returns discourage investment in U.S. assets.
Market Reaction: Traders closely follow Fed announcements to predict USD/JPY and EUR/USD movements.
2: ECB’s Influence on the Eurozone and EUR/USD
The European Central Bank (ECB) plays a crucial role in shaping the value of the euro and influencing the EUR/USD currency pair. Through interest rate changes, quantitative easing, and other monetary policies, the ECB directly impacts the forex market.
Raising interest rates: Strengthens the euro by attracting investment to euro-denominated assets.
Low interest rates or QE: Can weaken the euro, making it less attractive to global investors.
ECB’s focus on inflation: The ECB's primary concern with controlling inflation is often reflected in its monetary policy, which can affect the EUR/USD pair.
3: Bank of England (BoE) and GBP/USD Fluctuations
The Bank of England (BoE) has a significant influence on the British pound, especially against the USD. Similar to the Fed and ECB, the BoE's decisions on interest rates and other monetary policies create direct reactions in the forex market, especially the GBP/USD pair.
Raising interest rates: Tends to strengthen the British pound by encouraging investment.
Lower interest rates: Weakens the pound, as investors may look elsewhere for higher returns.
BoE's role in economic recovery: When the BoE signals tightening monetary policy, traders expect the GBP/USD to appreciate.
4: Central Bank Divergence and Forex Volatility
Divergence in monetary policies between central banks—such as the Fed and ECB—can lead to heightened forex market volatility. When one central bank adopts a more aggressive monetary stance (e.g., raising interest rates), and another takes a more dovish approach (e.g., lowering rates), significant currency fluctuations are often the result.
Fed vs. ECB policy divergence: A hawkish Fed and a dovish ECB can cause major volatility in the EUR/USD pair.
Interest rate spreads: A widening interest rate gap between the U.S. and the Eurozone often leads to stronger USD against the euro.
Market volatility: Traders closely monitor central bank actions to anticipate potential forex market fluctuations.
Geopolitical Events and Their Impact on Forex Volatility
Geopolitical events such as political instability, trade wars, and elections can significantly influence forex volatility. These events often create uncertainty, driving investors to react to potential risks, which leads to fluctuations in currency pairs like USD/TRY, EUR/USD, and GBP/USD.
1: Political Instability and Currency Depreciation
Geopolitical tensions, such as political instability or conflicts, can cause investors to flee from risky assets, leading to a depreciation of the local currency. In many cases, emerging market currencies like USD/TRY or USD/ZAR are particularly susceptible to these fluctuations.
Flight to safety: When political instability arises, investors often shift their capital to perceived safe-haven assets like the USD or JPY.
Emerging market impact: Currencies from emerging economies, such as TRY and ZAR, can face significant depreciation as investors worry about risk exposure.
Historical examples: Events like political upheaval in Turkey and South Africa often lead to rapid changes in currency values, particularly in USD/TRY and USD/ZAR pairs.
2: Trade Wars and Forex Market Reactions
Trade wars, such as the U.S.-China tariff disputes, disrupt global trade and lead to market volatility. Forex markets respond sharply to such tensions, particularly with currencies like the USD and CNY (Chinese Yuan).
Global uncertainty: Trade wars disrupt trade flows, creating an unpredictable economic environment that affects currency values.
USD and CNY fluctuations: In a trade conflict, the USD tends to rise due to its status as a global reserve currency, while the CNY often weakens due to economic pressures from tariffs.
Investor sentiment: As trade tensions heighten, market sentiment turns negative, leading to risk-off behavior and volatility in currency pairs such as USD/CNY and USD/JPY.
3: Elections and Currency Market Predictions
Elections often introduce uncertainty into the forex market, particularly when the economic policies of the winning candidate are unclear. In cases of major elections, like the U.S. presidential election or Brexit referendum, currency fluctuations can be dramatic, especially in pairs such as GBP/USD or USD/MXN.
Uncertainty post-election: Markets often experience volatility before and after elections, as traders react to potential policy changes.
Political outcomes and forex impact: A conservative win may favor the USD, while a more populist or protectionist agenda could hurt the GBP or MXN.
Market reactions: Forex traders closely monitor electoral results, especially in countries with significant economic power, such as the U.S. or the U.K.
Market Sentiment and Speculation in Forex Trading
Market sentiment and speculation are key drivers of forex market movements. Traders' risk appetite, speculation about future events, and investor confidence can all significantly influence currency fluctuations.
1: Risk Appetite and Currency Movements
Changes in investor risk appetite often lead to shifts in currency markets. When risk appetite is high, investors are more willing to invest in higher-yielding currencies, which can cause fluctuations in pairs like AUD/USD or USD/JPY.
Risk-on environment: During periods of economic optimism, investors gravitate towards riskier currencies like the AUD and NZD, as these offer higher returns.
Risk-off behavior: In uncertain times, investors tend to move toward safe-haven currencies like the USD and JPY, causing a drop in higher-yielding currencies.
Examples: For instance, AUD/USD tends to rise when global growth outlooks improve, but it weakens during global downturns or financial crises.
2: Speculation and Forex Market Dynamics
Speculation is a central element in forex trading, with traders anticipating future events like central bank actions or geopolitical shifts. This behavior can cause dramatic movements in currency values.
<1> Speculative strategies: Traders anticipate key economic reports, interest rate decisions, and geopolitical events, often acting before official announcements are made.
<2> Currency pair volatility: The USD/JPY or EUR/USD can experience substantial volatility when traders speculate on decisions by the Federal Reserve or European Central Bank (ECB).
<3> Impact of rumors and news: The forex market is highly sensitive to speculation, with traders reacting to rumors or geopolitical tensions, which can cause short-term volatility in currencies.
3: Investor Confidence and Exchange Rate Behavior
Investor confidence plays a pivotal role in shaping the forex market. When investors have strong faith in a country's economic outlook, demand for its currency rises, strengthening the exchange rate. Conversely, a loss of confidence can cause sharp declines.
High confidence, strong currency: Currencies like the USD and GBP typically strengthen when economic indicators (such as GDP growth, low inflation, or low unemployment) signal a healthy economy.
Loss of confidence, weaker currency: In times of uncertainty or economic downturns, investor confidence can plummet, leading to depreciation in currencies like USD/MXN or GBP/USD.
Example: Following Brexit, a loss of confidence in the UK economy led to a steep decline in the GBP, as investors feared economic instability.
4: Market Volatility and Trading Strategies
Volatility in the forex market presents both challenges and opportunities. Traders use various strategies to capitalize on market movements driven by volatility, whether short-term price swings or long-term trends.
Short-term volatility: Traders often use day trading or scalping strategies to take advantage of short-term market fluctuations.
Long-term volatility: For longer-term movements, traders may turn to position trading, relying on broader market trends and economic fundamentals.
Adjustment to news: Volatility increases during major news releases, such as non-farm payroll reports, central bank meetings, or geopolitical developments. Traders often adjust their strategies accordingly.
5: Sentiment Analysis in Forex Trading
Sentiment analysis is a crucial tool for forex traders, as it helps to gauge the collective psychology of the market. By understanding market sentiment, traders can anticipate future price movements and capitalize on trends.
Measuring sentiment: Tools like the Commitment of Traders report or social media sentiment analysis can help traders assess market mood and predict shifts in currency prices.
Bullish or bearish trends: Sentiment analysis can identify bullish or bearish market sentiment. A shift from a risk-on to a risk-off environment, for example, can trigger a movement in USD/JPY or AUD/USD.
Example: During the COVID-19 pandemic, sentiment was overwhelmingly negative, leading to a flight to safety and the strengthening of currencies like the USD and CHF.
6: Risk Management Strategies in Volatile Markets
In highly volatile forex markets, effective risk management is crucial to minimize losses and protect profits. Traders use a variety of techniques to manage risk, including stop-loss orders, diversification, and leverage control.
| Risk Management Strategy | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Stop-Loss Orders | Automatically closes a position at a pre-set price to limit losses. | A trader sets a stop-loss at 1.2000 for EUR/USD to limit losses if the price falls. |
| Take-Profit Orders | Locks in profits by automatically closing a position once a target price is reached. | A trader places a take-profit at 1.2500 for GBP/USD to secure gains before market reversals. |
| Diversification | Spreads risk by investing in multiple currency pairs or asset classes. | A trader diversifies by holding both USD/JPY and AUD/USD positions. |
| Leverage Control | Reduces exposure by controlling the amount of leverage used in trades. | Using 2x leverage instead of 10x minimizes risk in volatile markets. |
Technical Analysis in Predicting Forex Market Fluctuations
Technical analysis is crucial in predicting forex market fluctuations. Traders use various tools like support and resistance levels, moving averages, chart patterns, and oscillators to gain insights into potential currency movements and make informed trading decisions.
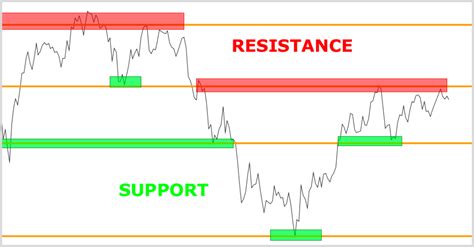
1: Support and Resistance Levels in Forex Trading
Support and resistance levels are fundamental concepts in technical analysis. These levels mark where price reversals are likely to occur, helping traders identify entry and exit points.
Support level: A price point where demand is strong enough to prevent the price from falling further. It is often seen as a floor for the price movement.
Resistance level: A price point where selling pressure is strong enough to prevent the price from rising further. It is often viewed as a ceiling for the price.
Breakouts: When the price breaks through a support or resistance level, it can indicate a significant price movement. Traders may use this to identify trends.
Example: In EUR/USD, if the price approaches a resistance level at 1.2000 and fails to break it, traders may anticipate a reversal towards 1.1900, a potential support level.
2: Moving Averages and Trend Analysis
Moving averages are essential tools in identifying market trends. By smoothing out price data over a specific period, they help traders assess both short-term and long-term price movements.
Simple Moving Average (SMA): The average of prices over a set number of periods. A 50-day SMA can help identify the medium-term trend.
Exponential Moving Average (EMA): Places more weight on recent prices, making it more sensitive to price changes. The USD/JPY may show a short-term upward trend through a 20-day EMA.
Trend indicators: Moving averages help identify whether a currency pair is trending upwards, downwards, or moving sideways.
Example: The GBP/USD often follows a predictable trend when its 100-day moving average is above the 200-day moving average, signaling an uptrend.
3: Chart Patterns and Forex Trading
Chart patterns are crucial for predicting forex market movements, offering insights into price behavior and potential future trends.
Head and Shoulders: A reversal pattern that signals the end of an uptrend or downtrend. A USD/CHF pair breaking the neckline after a head and shoulders pattern could indicate a bearish reversal.
Triangles: These patterns form when price moves within converging trendlines, signaling consolidation and possible breakout in either direction.
Flags and Pennants: Continuation patterns that indicate the market is likely to resume its previous trend after a brief period of consolidation.
Example: In the EUR/USD, a symmetrical triangle pattern might indicate a breakout in either direction, depending on which trendline is broken.
4: Oscillators and Indicators for Forex Market Analysis
Oscillators like the Relative Strength Index (RSI) and Stochastic indicators help traders identify overbought and oversold conditions, signaling potential reversals.
| Indicator | Description | Usage | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| RSI | Measures overbought or oversold conditions, ranging from 0 to 100. | RSI above 70 indicates overbought; below 30, oversold. | EUR/USD RSI at 80 suggests a potential reversal. |
| Stochastic | Compares the closing price to a range over a period. | A reading above 80 signals overbought; below 20 signals oversold. | GBP/USD Stochastic at 15 suggests a buying opportunity. |
| MACD | Measures the difference between a 12-day EMA and a 26-day EMA. | A crossover of MACD above the signal line can indicate a buy. | USD/JPY MACD crossover above the signal line suggests a bullish trend. |
| Bollinger Bands | Measures volatility and indicates overbought or oversold conditions based on standard deviations from a moving average. | Price moving outside the bands suggests extreme conditions. | AUD/USD moving above the upper Bollinger Band may indicate a sell. |
5: Combining Technical Analysis with Fundamental Data
For the most accurate predictions, many traders combine technical analysis with fundamental data, creating a comprehensive strategy. While technical analysis helps forecast market movements based on historical price patterns, fundamental analysis provides insights into the underlying economic forces.
Economic indicators: Key indicators like GDP growth, unemployment rate, and inflation often affect currency values. For instance, if the Federal Reserve raises interest rates, it might push the USD higher, which could be confirmed by a rising trend in moving averages.
Central bank actions: Decisions by central banks, such as the European Central Bank (ECB) or Bank of England (BoE), can provide significant market-moving data. Traders can use chart patterns like triangles and moving averages to assess potential breakouts after such announcements.
Example: Combining a USD/JPY chart pattern (e.g., ascending triangle) with a Federal Reserve rate hike might signal a strong upward movement in the pair, confirming the technical breakout with fundamental support.
Conclusion
As we've explored, forex market fluctuations are influenced by a complex web of factors, with changing income levels playing a pivotal role. These fluctuations are not solely driven by interest rates or central bank policies, but also by broader economic shifts tied to income growth and changes in purchasing power. Economic indicators such as inflation, GDP growth, and unemployment rates interact dynamically with currency pairs, shaping both short-term and long-term market movements. By closely monitoring these factors, traders and investors can gain deeper insights into the ever-changing forex landscape. In addition, understanding how geopolitical events, market sentiment, and trading strategies affect these fluctuations can help to develop more robust approaches to currency trading.
In sum, staying attuned to the shifts in income levels and how they ripple through economic systems is key to understanding and predicting forex market movements. Whether you're a seasoned trader or a newcomer to the market, integrating this knowledge into your strategy can make a significant difference in how you approach forex trading.