Introduction
In the dynamic world of forex trading, determining the best method of analysis is crucial for success. Traders often debate between various approaches, each with its unique advantages and disadvantages. This article will explore the primary methods of forex analysis—technical analysis, fundamental analysis, and sentiment analysis—providing insights and case studies to help both novice and experienced traders make informed decisions.
Technical Analysis
Overview
Technical analysis involves studying historical price charts and trading volumes to predict future market movements. This method is grounded in the belief that price movements are not random but follow identifiable patterns over time.
Key Tools and Indicators
Moving Averages: Used to smooth out price data and identify trends.
Relative Strength Index (RSI): Measures the speed and change of price movements, indicating overbought or oversold conditions.
Bollinger Bands: Help in identifying market volatility and potential price reversals.
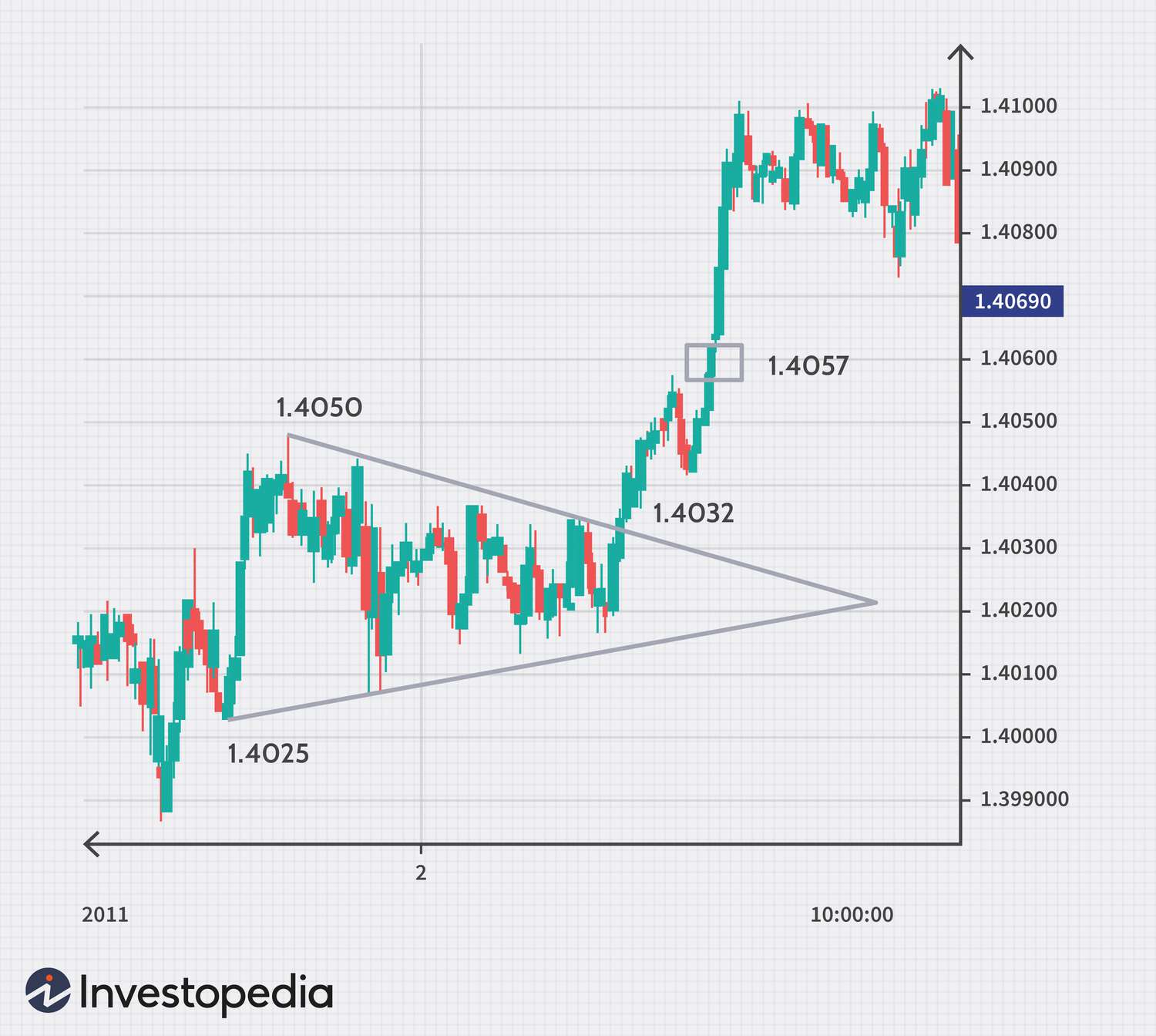
Case Study: EUR/USD and Moving Averages
In 2020, a trader using the 50-day and 200-day moving averages noticed a "golden cross" on the EUR/USD chart, where the 50-day moving average crossed above the 200-day moving average. This technical signal often indicates a bullish trend. The trader entered a long position and benefited from a subsequent 5% rise in the EUR/USD pair over the next three months.
User Feedback
Many traders appreciate technical analysis for its simplicity and the ability to automate trading strategies using software. However, some caution that it can lead to false signals in volatile markets.
Fundamental Analysis
Overview
Fundamental analysis examines economic, financial, and other qualitative and quantitative factors to evaluate the intrinsic value of a currency. This method involves analyzing indicators such as GDP growth, interest rates, inflation, and political stability.
Key Economic Indicators
Gross Domestic Product (GDP): Reflects the economic health of a country.
Interest Rates: Set by central banks, they influence currency strength.
Inflation Rates: High inflation can depreciate a currency’s value.
Employment Data: Strong employment figures generally strengthen a currency.
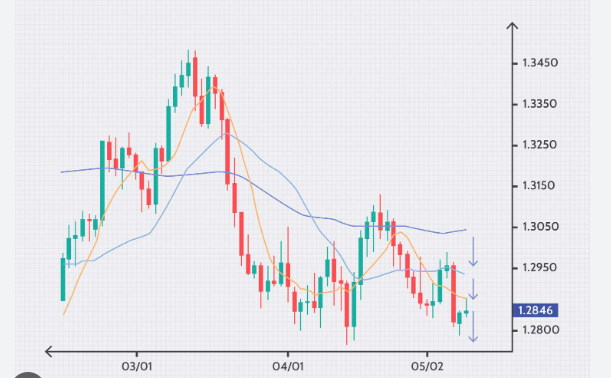
Case Study: The Impact of Brexit on GBP
The Brexit referendum in 2016 provides a compelling case study for fundamental analysis. The uncertainty surrounding the UK's departure from the EU caused significant volatility in the British Pound (GBP). Analysts who anticipated economic challenges post-Brexit shorted the GBP, resulting in substantial profits as the currency dropped sharply following the referendum.
User Feedback
Fundamental analysis is praised for its comprehensive approach, considering a wide range of factors. However, it requires staying updated with global economic news, which can be time-consuming.
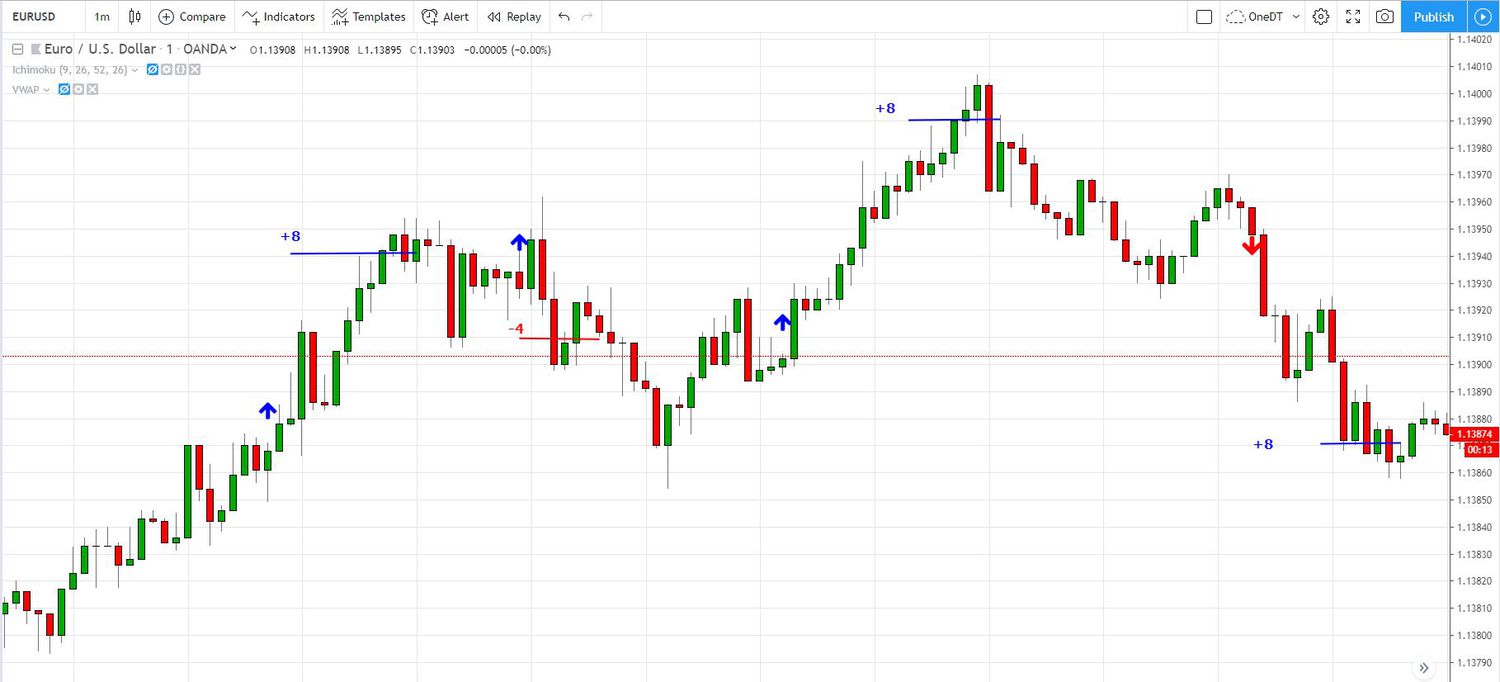
Sentiment Analysis
Overview
Sentiment analysis gauges the market's mood by analyzing the positions and opinions of traders. It is based on the premise that market movements are influenced by the collective behavior and psychology of market participants.
Tools and Indicators
Commitment of Traders (COT) Report: Provides insights into the positions of various market participants.
Sentiment Indexes: Measure the overall market sentiment, often indicating bullish or bearish tendencies.
Case Study: USD/JPY and the COT Report
In early 2021, sentiment analysis using the COT report indicated that institutional traders were heavily long on the Japanese Yen (JPY) against the US Dollar (USD). This contrarian indicator suggested that the USD/JPY might soon reverse. Traders who acted on this information saw significant gains when the USD/JPY pair indeed reversed its trend shortly thereafter.
User Feedback
Sentiment analysis is valued for its ability to provide a contrarian view, often highlighting potential market reversals. However, its effectiveness can be limited in highly manipulated or low-liquidity markets.
Comparison of Analysis Methods
Trends in the Industry
The forex industry has seen a growing trend towards integrating multiple methods of analysis. This holistic approach allows traders to cross-verify signals and make more informed decisions. For instance, combining technical analysis with fundamental insights can provide a clearer picture of market conditions.
Statistical Insights
According to a survey by the Bank for International Settlements, over 70% of forex traders use some form of technical analysis, while 60% incorporate fundamental analysis in their trading strategies. Sentiment analysis, though less prevalent, is gaining traction, especially among retail traders.
Professional Opinions
Many professional traders recommend a balanced approach. For example, George Soros, a renowned forex trader, often combines fundamental analysis with technical signals to time his trades effectively.
Conclusion
Determining the best method of analysis for forex trading depends on individual preferences and trading styles. Technical analysis offers a systematic approach to understanding price movements, fundamental analysis provides insights into the underlying economic forces, and sentiment analysis captures the market's psychological aspects. Combining these methods can enhance trading decisions, providing a more comprehensive view of the forex market.
Get the most out of your trading with exclusive offers from Best Forex Rebates!